Featured Articles
|
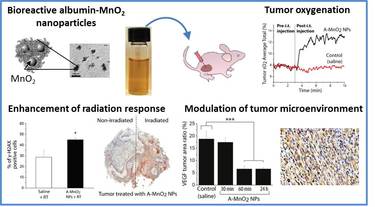
Multifunctional Albumin-MnO2 Nanoparticles Modulate Solid Tumor Microenvironment by Attenuating Hypoxia, Acidosis, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Enhance Radiation Response.
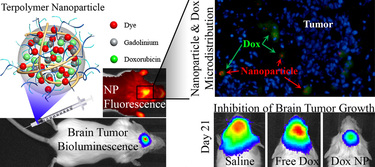
ACS Nano 2014 A Multifunctional Polymeric Nanotheranostic System Delivers Doxorubicin and Imaging Agents across the Blood-Brain Barrier Targeting Brain Metastases of Breast Cancer. ACS Nano 2014 Hybrid Nanoparticles: Design of Hybrid MnO2-Polymer-Lipid Nanoparticles with Tunable Oxygen Generation Rates and Tumor Accumulation for Cancer Treatment Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015 |
Publications & Book Chapters
2009 - 2015
- R.X. Zhang, P. Cai, T. Zhang, K. Chen, J. Li, J. Cheng, K.S. Pang, A.M Rauth, X.Y. Wu, Polymer-lipid hybrid nanoparticles synchronize pharmacokinetics of co-encapsulated doxorubicin-mitomycin C and enable their spatiotemporal co-delivery and local bioavailability in breast
tumor, Nanomedicine, 2016 - Y. Li, N. Taulier, M.R. Abbaspour, P. Grootenrst, A.M. Rauth, X.Y. Wu, Optimization of controlled release nanoparticle formulation of
verapamil hydrochloride using artificial neural networks with genetic algorithm and response surface methodology, Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015, 94, 170-179 - J. Chen, J. Li, C. Gordijo, M. Chu, Y. Sun, X.Y. Wu, Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery Microchips, in Encyclopedia of Nanotechnology (2nd ed), Chapter ID 390, 2015
- Y-H. Ma, Q. Wang, J. Gong, X.Y. Wu, Formulation of granules for site-specific delivery of antimicrobial essential oil to the animal GI tract, J. Pharm. Sci. 2015
- A.Z. Abbasi, P. Prasad, P. Cai, C. He, W.D. Foltz, M.A. Amini, C.R. Gordijo, A.M. Rauth, X.Y. Wu, Manganese oxide and docetaxel co-loaded fluorescent polymer nanoparticles for dual modal imaging and chemotherapy of breast cancer, J. Control. Release 2015, 209, 186-196.
- J. Cheng, Q. Liu, A.J. Shuhendler, A.M. Rauth, X. Y. Wu, Optimizing the Design and In Vitro Evaluation of Bioreactive Glucose Oxidase-Microspheres for Enhanced Cytotoxicity against Multidrug Resistant Breast Cancer Cells, Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 1(130),164-172.
- C. Gordijo, X.Y. Wu, A new life to an old material, Materials Today 2015
- C. Gordijo*, A.Z. Abbasi*, M.A. Amini, H.Y. Lip, A. Maeda, P. Cai, P.J. O?Brien, R.S. DaCosta, A.M. Rauth , X.Y. Wu, Design of hybrid MnO2-polymer-lipid nanoparticles with tunable oxygen generation rate and tumor accumulation for cancer treatment, Adv Func Mater. 10.1002/adfm.201404511 (Frontispiece and editorial highlight)
- J. Li, M. K.L. Chu, C. R. Gordijo, A. Z. Abbasi, K. Chen, H. A. Adissu, A. Giacca, O. Plettenburg, M. Lohn, X.Y. Wu, Microfabricated microporous membranes reduce the host immune response and prolong the functional lifetime of a closed-loop insulin delivery implant in a type 1 diabetic rat model, Biomaterials 2015, 47, 51-61.
-
2008 and Before
- Liu, J., Scollard, D. A., Reilly, R. M., Wu, X. Y., & Johnston, M. R. (2008). Effect of particle size on the lymphatic distribution of 111Indium-aminopolystyrene through intrapleural administration. Lymphology, 41(4), 153-160.
- Kim, K., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Cheng, J., Wu, X. Y., & Sun, Y. (2008). Mechanical characterization of polymeric microcapsules using a force-feedback MEMS microgripper. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS'08 - "Personalized Healthcare through Technology", 1845-1848.
- Kim, K., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Cheng, J., Wu, X. Y., & Sun, Y. (2008). Mechanical characterization of polymeric microcapsules using a force-feedback MEMS microgripper. Conference Proceedings : ...Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society.IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society.Conference, 2008, 1845-1848.
- Chattopadhyay, N., Zastre, J., Wong, H. -., Wu, X. Y., & Bendayan, R. (2008). Solid lipid nanoparticles enhance the delivery of the HIV protease inhibitor, atazanavir, by a human brain endothelial cell line. Pharmaceutical Research, 25(10), 2262-2271.
- Kim, K., Cheng, J., Liu, Q., Wu, X. Y., & Sun, Y. (2008). MEMS capacitive force sensors for micro-scale compression testing of biomaterials. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), 888-891.
- Li, Y., Wong, H. L., Shuhendler, A. J., Rauth, A. M., & Wu, X. Y. (2008). Molecular interactions, internal structure and drug release kinetics of rationally developed polymer-lipid hybrid nanoparticles. Journal of Controlled Release, 128(1), 60-70.
- Huang, H. Y., Shaw, J., Yip, C., & Wu, X. Y. (2007). Microdomain pH gradient and kinetics inside composite polymeric membranes of pH and glucose sensitivity. Pharmaceutical Research, 25(5), 1150-1157.
- A.J. Shuhendler, P. O’Brien, A.M. Rauth, X.Y. Wu (2008) On the synergistic effect of doxorubicin and mitomycin C against breast cancer cells, Drug Metabolism and Drug Interactions, 22 (4), 201-233.
- Abdekhodaie, M. J., & Wu, X. Y. (2008). Drug release from ion-exchange microspheres: Mathematical modeling and experimental verification. Biomaterials, 29(11), 1654-1663.
- Moselhy, J., Sarkar, S., Chia, M. C., Mocanu, J. D., Taulier, N., Liu, F. F., et al. (2007). Evaluation of copolymers of N-isopropylacrylamide and 2-dimethyl(aminoethyl)methacrylate in nonviral and adenoviral vectors for gene delivery to nasopharyngeal carcinoma. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2(3), 461-478.
- Liu, Q., Rauth, A. M., & Wu, X. Y. (2007). Immobilization and bioactivity of glucose oxidase in hydrogel microspheres formulated by an emulsification-internal gelation-adsorption-polyelectrolyte coating method. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 339(1-2), 148-156.
- Wong, H. L., Bendayan, R., Rauth, A. M., Li, Y., & Wu, X. Y. (2007). Chemotherapy with anticancer drugs encapsulated in solid lipid nanoparticles. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 59(6), 491-504.
- Liu, J., Meisner, D., Kwong, E., Wu, X. Y., & Johnston, M. R. (2007). A novel trans-lymphatic drug delivery system: Implantable gelatin sponge impregnated with PLGA-paclitaxel microspheres. Biomaterials, 28(21), 3236-3244.
- Wong, H. L., Rauth, A. M., Bendayan, R., & Wu, X. Y. (2007). In vivo evaluation of a new polymer-lipid hybrid nanoparticle (PLN) formulation of doxorubicin in a murine solid tumor model. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 65(3), 300-308.
- Wong, H. L., Bendayan, R., Rauth, A. M., & Wu, X. Y. (2006). Simultaneous delivery of doxorubicin and GG918 (elacridar) by new polymer-lipid hybrid nanoparticles (PLN) for enhanced treatment of multidrug-resistant breast cancer. Journal of Controlled Release, 116(3), 275-284.
- Wong H.L., Li Y., Bendayan R., Rauth A.M., Wu X.Y. (2006) Solid lipid nanoparticles for cancer chemotherapy, in: Nanotechnology for Cancer Therapy, CRC Press, pp.714-776 (on invitation).
- Li, Y., Taulier, N., Rauth, A. M., & Wu, X. Y. (2006). Screening of lipid carriers and characterization of drug-polymer-lipid interactions for the rational design of polymer-lipid hybrid nanoparticles (PLN). Pharmaceutical Research, 23(8), 1877-1887.
- Abdekhodaie, M. J., & Wu, X. Y. (2006). Drug loading onto ion-exchange microspheres: Modeling study and experimental verification. Biomaterials, 27(19), 3652-3662.
- Wong, H. L., Rauth, A. M., Bendayan, R., Manias, J. L., Ramaswamy, M., Liu, Z., et al. (2006). A new polymer-lipid hybrid nanoparticle system increases cytotoxicity of doxorubicin against multidrug-resistant human breast cancer cells. Pharmaceutical Research, 23(7), 1574-1585.
- Cheung, R. Y., Rauth, A. M., Ronaldson, P. T., Bendayan, R., & Wu, X. Y. (2006). In vitro toxicity to breast cancer cells of microsphere-delivered mitomycin C and its combination with doxorubicin. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 62(3), 321-331.
- Liu, J., Wong, H. -., Moselhy, J., Bowen, B., Wu, X. Y., & Johnston, M. R. (2006). Targeting colloidal particulates to thoracic lymph nodes. Lung Cancer, 51(3), 377-386.
- Cheung, R. Y., Ying, Y., Rauth, A. M., Marcon, N., & Wu, X. Y. (2005). Biodegradable dextran-based microspheres for delivery of anticancer drug mitomycin C. Biomaterials, 26(26), 5375-5385.
- Abdekhodaie, M. J., & Wu, X. Y. (2005). Modeling of a cationic glucose-sensitive membrane with consideration of oxygen limitation. Journal of Membrane Science, 254(1-2), 119-127.
- Cheung, R. Y., Rauth, A. M., & Wu, X. Y. (2005). In vivo efficacy and toxicity of intratumorally delivered mitomycin C and its combination with doxorubicin using microsphere formulations. Anti-Cancer Drugs, 16(4), 423-433.
- Li, Y., Rauth, A. M., & Wu, X. Y. (2005). Prediction of kinetics of doxorubicin release from sulfopropyl dextran ion-exchange microspheres using artificial neural networks. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 24(5), 401-410.
- Zhou, Y., Chu, J. S., Zhou, T., & Wu, X. Y. (2005). Modeling of dispersed-drug release from two-dimensional matrix tablets. Biomaterials, 26(8), 945-952.
- Cheung, R. Y., Kuba, R., Rauth, A. M., & Wu, X. Y. (2004). A new approach to the in vivo and in vitro investigation of drug release from locoregionally delivered microspheres. Journal of Controlled Release, 100(1), 121-133.
- Zhang, K., & Wu, X. Y. (2004). Temperature and pH-responsive polymeric composite membranes for controlled delivery of proteins and peptides. Biomaterials, 25(22), 5281-5291.
- Wong, H. L., Bendayan, R., Rauth, A. M., & Wu, X. Y. (2004). Development of solid lipid nanoparticles containing ionically complexed chemotherapeutic drugs and chemosensitizers. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 93(8), 1993-2008.
- Wu, Z. H., Sun, M., Mei, X. Y., & Ruda, H. E. (2004). Growth and photoluminescence characteristics of AlGaAs nanowires. Applied Physics Letters, 85(4), 657-659.
- ZHang, K., Huang, H., Yang, G., Shaw, J., Yip, C., & Wu, X. Y. (2004). Characterization of nanostructure of stimuli-responsive polymeric composite membranes. Biomacromolecules, 5(4), 1248-1255.
- Zhou, Y., Chu, J. S., & Wu, X. Y. (2004). Theoretical analysis of drug release into a finite medium from sphere ensembles with various size and concentration distributions. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 22(4), 251-259.
- Zhang, K., Quan, C., Huang, H., Taulier, N., & Wu, X. Y. (2004). On the stability of insulin delivered through a new glucose-responsive polymeric composite membrane. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 56(5), 611-620.
- Liu, Z., Ballinger, J. R., Rauth, A. M., Bendayan, R., & Wu, X. Y. (2003). Delivery of an anticancer drug and a chemosensitizer to murine breast sarcoma by intratumoral injection of sulfoprophyl dextran microspheres. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 55(8), 1063-1073.
- Wu X.Y. and Yam F., Polymer system for drug delivery and solute separation, US patent No. 6,565,872 (May 2003).
- Zhou, Y., & Wu, X. Y. (2003). Modeling and analysis of dispersed-drug release into a finite medium from sphere ensembles with a boundary layer. Journal of Controlled Release, 90(1), 23-36.
- Wu X.Y., Zhang Q. and Arshady R. (2003) Stimuli Sensitive Hydrogels. Polymer Structure and Phase Transition (invited review chapter) in: Polymeric Biomaterials, R. Arshady (Ed.), Citus Books, London, UK, p157-194.
- Wu X.Y., Zhang Q. and Arshady R. (2003) Stimuli Sensitive Hydrogels. Response and Release Modulation (invited review chapter) in: Polymeric Biomaterials, R. Arshady (Ed.), Citus Books, London, UK, p195-231.
- Zhou, Y., & Wu, X. Y. (2002). Theoretical analyses of dispersed-drug release from planar matrices with a boundary layer in a finite medium. Journal of Controlled Release, 84(1-2), 1-13.
- Zhang, K., & Wu, X. Y. (2002). Modulated insulin permeation across a glucose-sensitive polymeric composite membrane. Journal of Controlled Release, 80(1-3), 169-178.
- Liu, Z., Cheung, R., Wu, X. Y., Ballinger, J. R., Bendayan, R., & Rauth, A. M. (2001). A study of doxorubicin loading onto and release from sulfopropyl dextran ion-exchange microspheres. Journal of Controlled Release, 77(3), 213-224.
- Liu, Z., Bendayan, R., & Wu, X. Y. (2001). Triton-X-100-modified polymer and microspheres for reversal of multidrug resistance. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 53(6), 779-787.
- Yam, F., Wu, X. Y., & Zhang, Q. (2000). A novel composite membrane for temperature-and pH-responsive permeation
- Lenet, B. J., Komorowski, R., Wu, X. Y., Huang, J., Grad, H., Lawrence, H. P., et al. (2000). Antimicrobial substantivity of bovine root dentin exposed to different chlorhexidine delivery vehicles. Journal of Endodontics, 26(11), 652-655.
- Liu, Z., Wu, X. Y., Ballinger, J. R., & Bendayan, R. (2000). Synthesis and characterization of surface-hydrophobic ion-exchange microspheres and the effect of coating on drug release rate. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 89(6), 807-817.
- Huang, J., Wong, H. -., Zhou, Y., Wu, X. Y., Grad, H., Komorowski, R., et al. (2000). In vitro studies and modeling of a controlled-release device for root canal therapy. Journal of Controlled Release, 67(2-3), 293-307.
- Huang, J., Kao, H., & Wu, X. Y. (2000). The pH-dependent biphasic release of azidothymidine from a layered composite of PVA disks and P(MMA/MAA) spheres. Journal of Controlled Release, 67(1), 45-54.
- Komorowski, R., Grad, H., Wu, X. Y., & Friedman, S. (2000). Antimicrobial substantivity of chlorhexidine-treated bovine root dentin. Journal of Endodontics, 26(6), 315-317.
- Moselhy, J., Wu, X. Y., Nicholov, R., & Kodaria, K. (2000). In vitro studies of the interaction of poly(NIPAm/MAA) nanoparticles with proteins and cells. Journal of Biomaterials Science, Polymer Edition, 11(2), 123-147.
- Li, J. -., Zhou, Y., Wu, X. Y., Odidi, I., & Odidi, A. (2000). Characterization of wet masses of pharmaceutical powders by triaxial compression test. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 89(2), 178-190.
- Wu, X. Y., & Lee, P. I. (2000). Preparation and characterization of inulin ester microspheres as drug carriers. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 77(4), 833-840.
- Q. Zhang, L. Liu, X.Y. Wu, K. Yao (2000) pH-responsive swelling behavior of collagen complex materials, Art. Cells Blood Subs. Immob. Biotech. 28, 255-262.
- F. Yam, X.Y. Wu and Q. Zhang (2000) A novel composite membrane for temperature and pH responsive permeation, in: Controlled Drug Delivery: Designing Technology for the Future, Ed. K. Park, ACS, Washington, DC, pp. 263-272.
- Y. Sun, H. Zhou, Q. Zhang, X.Y. Wu (2000) Improved controlled release study of lomustine, Art. Cell, Blood Subs. Immob. Biotech. 28, 173-180.
- Wu, X. Y., & Zhou, Y. (1999). Studies of diffusional release of a dispersed solute from polymeric matrixes by finite element method. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 88(10), 1050-1057.
- Huang, J., & Wu, X. Y. (1999). Effects of pH, salt, surfactant and composition on phase transition of poly(NIPAm/MAA) nanoparticles. Journal of Polymer Science, Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 37(14), 2667-2676.
- Ly, J., & Wu, X. Y. (1999). Bimodal release of theophylline from 'seed-matrix' beads made of acrylic polymers. Pharmaceutical Development and Technology, 4(2), 257-267.
- Liu, Z., Wu, X. Y., & Bendayan, R. (1999). In vitro investigation of ionic polysaccharide microspheres for simultaneous delivery of chemosensitizer and antineoplastic agent to multidrug-resistant cells. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 88(4), 412-418.
- Wu, X. Y., & Zhou, Y. (1999). Simulation of diffusional release of a dispersed solute from polymeric matrices into a finite volume. Proceedings of the Controlled Release Society, (26), 1016-1017.
- Yam F. and Wu X.Y. (1999) A novel composite membrane for temperature responsive permeation, Polymer Preprint, 40, 312-313.
- Wu, X. Y., Eshun, G., & Zhou, Y. (1998). Effect of interparticulate interaction on release kinetics of microsphere ensembles. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 87(5), 586-593.
- Wu, X. Y., & Zhou, Y. (1998). Finite element analysis of diffusional drug release from complex matrix systems. II. factors influencing release kinetics. Journal of Controlled Release, 51(1), 57-71.
- Wu, X. Y., & Zhou, Y. (1998). Numerical analysis of drug release from matrix tablets with moving boundaries. Proceedings of the Controlled Release Society, (25), 451-452.
- Wu, X. Y., Zhou, Y., & Eshun, G. (1998). Influence of drug accumulation and particle separation on release kinetics of multiparticulate systems. Proceedings of the Controlled Release Society, (25), 449-450.
- Wu, X. Y., Ly, J., & Zhou, Y. (1998). Modeling of bimodal release from composite polymeric beads. Proceedings of the Controlled Release Society, (25), 447-448.
- Huang, J., Wong, H. L., Wu, X. Y., Grad, H. A., Komorowski, R., & Friedman, S. (1998). A device for controlled release of antibacterial drugs for dental root canal therapy. Proceedings of the Controlled Release Society, (25), 778-779.
- Zhou, Y., & Wu, X. Y. (1997). Finite element analysis of diffusional drug release from complex matrix systems. I. complex geometries and composite structures. Journal of Controlled Release, 49(2-3), 277-288.
- Subotic, D. V., & Wu, X. Y. (1997). Interactions of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid) with poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone). Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 36(4), 1302-1309.
- Pelton R.H., Wu X.Y., McPhee W., and Tam K.C., The preparation and characterization of polyNIPAM latexes, in: Colloidal polymer particles, Ed. J.W. Goodwin and R. Buscall, Academic Press, pp.81-99 (1995).
- Wu X.Y., Pelton R.H., Hamielec A.E., Woods D.R., and McPhee W., The kinetics of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgel latex formation, Colloid Polym. Sci. 272, 467-477 (1994).
- Hunkeler D., Wu X.Y. and Hamielec A.E., Pelton R.H., and Woods D.R., Characterization of polyacrylamide-co-sodium acrylate, in: Macro-Ion Characterization, From Dilute Solutions to Complex Fluids, Ed. K.S. Schmitz, pp.162-177 (1994).
- Wu, X. Y., & Lee, P. I. (1993). Preparation and characterization of thermal- and pH-sensitive nanospheres. Pharmaceutical Research, 10(10), 1544-1547.
- Wu X.Y., Pelton R.H., Tam K.C., Woods D.R., and Hamielec A.E. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). I. Interactions with sodium dodecyl sulphate measured by conductivity, J. Polym. Sci.: Part A: Polym. Chem. 31, 957-962 (1993).
- Tam K.C., Wu X.Y., and Pelton R.H., Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). II. Effect of polymer concentration, temperature, and surfactant on the viscosity of aqueous solutions, J. Polym. Sci.: Part A: Polym. Chem., 31, 963-969 (1993).
- Hunkeler D., Wu X.Y. and Hamielec A.E., Molecular weight characterization of poly(acrylamide-co-sodium acrylate) II. Light scattering, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 46, 649-657 (1992).
- Tam K.C., Wu X.Y. and Pelton R.H., Viscometry - A useful tool for studying conformational changes of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) in solutions, Polymer Communications, 33, 436-438 (1992).
- Hunkeler D., Wu X.Y. and Hamielec A.E., Characterization of polyelectrolytes, in: Polyelectrolyte Gels, Properties, Preparation, and Applications, Ed. R.S. Harland and R.K. Prud'homme, pp.53-79 (1992).
- Wu X.Y., Hunkeler D., Hamielec A.E., Pelton R.H. and Woods D.R., Molecular weight characterization of poly(acrylamide-co-sodium acrylate) I. Viscometry, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 42, 2081-2093 (1991).
- Wu X.Y., Hunkeler D., Hamielec A.E. and Pelton R., Molecular weight characterization of polyelectrolytes, Polymer Materials Sci. Eng. 58, 792-794 (1988).
Patents & Copyrights
- X.Y. Wu and F. Yam, CA patent
No. 2,262,073 (issued in March 2009) Polymeric System for Drug Delivery and Solute
Separation.
- J. Liu, M. Johnston, X.Y. Wu,
PCT/CA2006/001321 Methods and devices for lymphatic targeting (PCT Application).
- J. Liu, M. Johnston, X.Y. Wu,
US 12/063,614. Methods and devices for lymphatic targeting (USA).
- J. Liu, M. Johnston, X.Y. Wu,
CA 2,618,807 Methods and devices for lymphatic targeting (Canada).
- J. Liu, M. Johnston, X.Y. Wu,
EP2006000775100 (Publication# EP1922094A1) Methods and devices for lymphatic targeting
(Europe).
- J. Liu, M. Johnston, X.Y. Wu,
CN200680038249.5 Methods and devices for lymphatic targeting (China).
- J. Liu, M. Johnston, X.Y. Wu,
IN 2108/DELNP/2008 Methods and devices for lymphatic targeting (India).
- J. Liu, M. Johnston, X.Y. Wu,
200680038249.5 Methods and devices for lymphatic targeting (Hong Kong).
- J. Liu, M. Johnston, X.Y. Wu,
US60/707,534 Lymphatic Targeting (US Provisional Application).
- X.Y. Wu, C. Gordijo, K.
Zhang, H. Huang, US 61/331,690 Insulin delivery device (US Provisional Application).